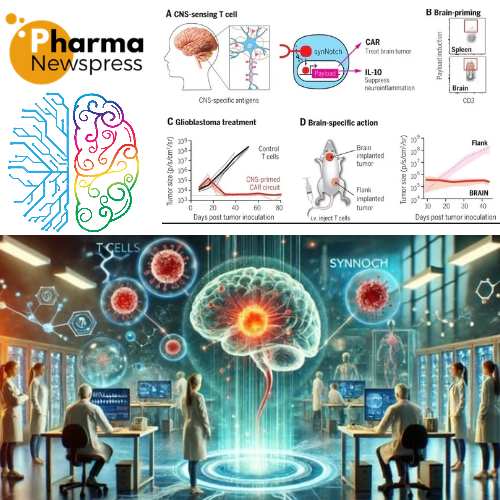
The study published in Science highlights a significant breakthrough in using synNotch technology to transform T cells for treating neurological diseases, overcoming challenges posed by the blood-brain barrier.
Unlike many drugs, T cells can naturally cross this barrier, making them an attractive vehicle for targeted therapies.

Key Points of the Research:
✏️. SynNotch Technology:
🔹Initially proposed in 2016 to address limitations in traditional CAR-T or TCR-T therapies.
🔹Uses engineered Notch receptors for enhanced target recognition and safety by adding an extra precision layer to immune recognition.
🔹Enables flexible drug delivery by adjusting the therapeutic payload.
✏️.Targeting Brain-Specific Proteins:
🔹The research identified brevican (BCAN), a brain-specific extracellular matrix protein, as a precise target for synNotch receptors.
🔹BCAN was chosen after screening
🔹CNS-specific extracellular ligands.
✏️.Experimental Results:
🔹 Combined anti-BCAN synNotch with anti-EphA2/IL13R02 CAR-T therapy:
🔹Demonstrated effective treatment of glioblastoma and breast cancer brain metastases in mice.
🔹Achieved significant therapeutic outcomes with minimal off-target effects on tissues outside the brain.
✏️.Applied interleukin-10 (IL-10) as a payload:
🔹Showed remarkable improvement in neuroinflammatory conditions in mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.
✏️.Potential Applications:
🔹Precision treatment for primary and secondary brain cancers.
🔹Effective management of neuroinflammatory diseases.
🔹Possible extension to treating neurodegenerative diseases, suggesting vast clinical possibilities.
Clinical Implications:
The study underscores synNotch technology’s versatility and adaptability, offering a safer and more effective approach to address challenging neurological diseases.
The ability to specifically target CNS lesions while minimizing systemic side effects marks a substantial step toward precision medicine for brain disorders.minimizing systemic side effects marks a substantial step toward precision medicine for brain disorders.